As a result, the proportion of machine-to-machine (M2M) fees generated from non-connectivity services is expected to increase from an average of 21% in 2013 to over half (53%) by 2016 says analyst Morgan Mullooly in a new report from Analysys Mason in Cambridge.
The threat of decreasing connectivity revenue, which mobile network operators (MNOs) have been confronting on the consumer retail side of their businesses in the past few years, is beginning to emerge in the M2M sector as it matures and competition intensifies. Operators are moving up the M2M value chain and delivering end-to-end solutions, rather than just simple connectivity, in an effort to combat this trend.
With billions of things – cars, utility meters, TVs and even furniture – linked via the Internet and sending information about their status and condition, operators need to determine what role they will play in this ecosystem he says.
Many verticals and industries are adopting M2M technology to connect many different devices and machines. As a result, M2M has gained significant traction as a new business area for MNOs. Operators are well placed to provide the near-ubiquitous connectivity needed to maintain links between modules and sensors and to help drive business transformation for their clients but the M2M connectivity sector is maturing. Enterprises have had only a few choices when procuring an M2M solution, but more and more MNOs are launching services for this market. Competition for connectivity is also coming from dedicated M2M MVNOs, satellite connectivity providers and other connectivity service providers using dedicated, non-cellular spectrum.
The margins associated with connectivity will be squeezed as competition increases. The proliferation of new M2M applications that use 3G and 4G networks and generate high data usage, such as video surveillance or connected car services, could offset declines in connectivity revenue. Nevertheless, MNOs will face the challenge of remaining competitive while M2M connectivity is becoming commoditized and connectivity margins threaten to stagnate or shrink he says.
Most operators have recognized this, and are moving up the value chain by offering M2M solutions that combine connectivity with partners’ hardware or software, according to the results of a recent Analysys Mason survey.
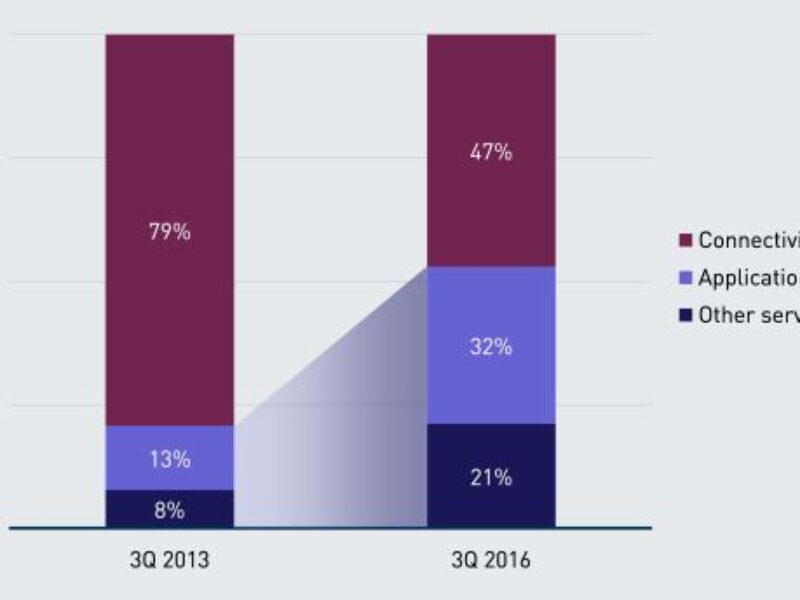
Ten leading global operators indicated that they expect non-connectivity services to account for more than half of the average revenue per connection (ARPC) from M2M services by 2016 (see Figure 1). Connectivity is expected to remain the largest single component of M2M revenue because it is the cornerstone of MNOs’ M2M businesses, but its share will decline from an average of 79% in 3Q 2013 to just 47% in 3Q 2016.
Operators’ transition from pure connectivity providers to end-to-end (E2E) M2M solution providers is one of the primary drivers behind this evolution and is based largely on cloud services. Many operators have assembled E2E product portfolios that will enable them to generate more value-added-services revenue. They will continue to develop new collaborations and launch new strategic partnerships models – including those with application developers and systems integrators, which are often essential partners for delivering E2E services.
www.analysysmason.com
Related stories:
Lost in Big Data: digital zombies
Wireless M2M connection market booms
Application enablement platform for IoT and M2M
Video surveillance boasts 3G connection in Sochi
Opening up the cloud for IoT
M2M module offers cost-effective migration from 2G to 3G
Deutsche Telekom launches M2M developer community
Wideband CMOS RF chip aims for M2M software radio
 If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News
If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News





