De-RISC updates its RISC-V space project
A project developing the first RISC-V fully European platform for aerospace has released the open source virtualisation extensions for a multicore processor design
The De-RISC Project ((Dependable Real-time Infrastructure for Safety-critical Computer) is two years into a three year development of a market-ready multi-core hardware-software platform based on the RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) with an efficient time and space partitioning hypervisor.
The four members of the consortium have been developing the different hardware and software alongside the validation strategy to will cover the different tests required to ensure that the system adheres to specification. This is key part of an independent European space capability that that does not rely on exernal technologies as part of the new EU space strategy.
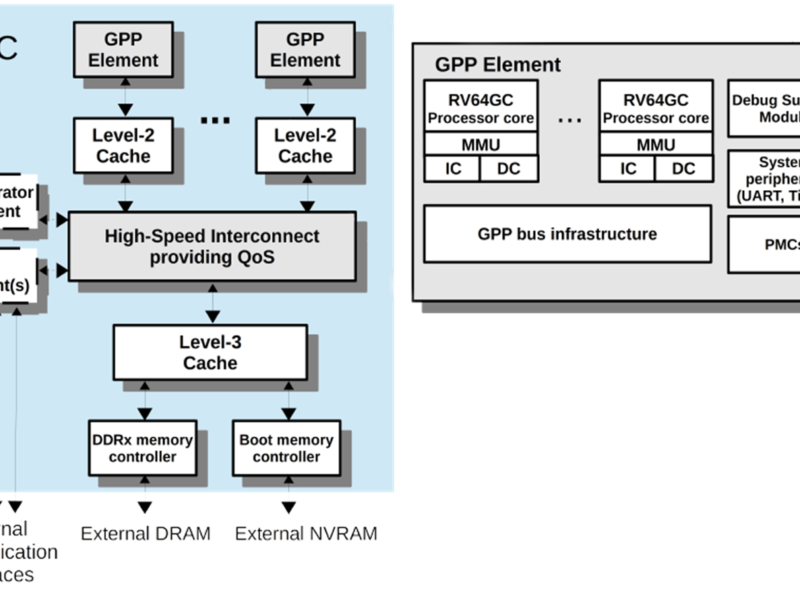
The consortium has released the NOEL-V RISC-V processor model extensions, notably the H extensions supporting full virtualization. The statistics unit for monitoring multicore interference has been released as open source as well.
- A RISC-V fully European platform for space
- First steps to European multicore RISC-V chip for space
- Europe in €13bn space shake up
The multicore interference element detects and measures the interference between different processor cores when they access the shared bus. This enables the user to have a better estimate of the worst-case execution times of critical applications thereby providing appropriate values to the timing analysis tool. This ensures that the real-time constraints of the critical applications running in the platform will be met.
The characterization of timing interference in a multi-core architecture is performed by using stressing benchmark applications, designed to apply a configurable amount of repeated transactions to a specific part of the memory.
By running an application under test, which can be a stressing benchmark itself, with a variable but precisely known number of concurrent accesses from other cores, and by measuring the distribution of its execution time, it is possible to evaluate the sensitivity to contention of a particular shared path.
On the software side, the consortium is developing benchmarks, the on-board satellite software stack which will use the LVCUGEN framework by CNES, and the Command and Data-Handling use-cases. Furthermore, the port of the hyperspectral image compression algorithm on the RISC-V platform is ongoing and it is expected to deliver results in the following months.
The multicore system-on-chip is being designed by Cobham Gaisler and the space partitioning hypervisor is based on the XtratuM hypervisor from FentISS in Spaon.
The XtratuM hypervisor has been selected for different space missions including the OneWeb satellite constellation, the PLATiNO generic satellite for constellations, and ARGOS-NEO ANGELS, EyeSat, SVOM, JUICE and MMX among others. The microprocessors developed by Cobham Gaisler have been used in a variety of ESA and NASA missions. Barcelona Supercomputing Center is one of the leading research institutions in Europe and has closely collaborated with Gaisler and Thales in European projects such as SAFURE and PROXIMA.
Next: RISC-V use cases for space
The consortium has defined the three use cases which will be executed in the project. These cover the execution of low-level benchmarks, an on-board satellite software stack, and a Command & Data Handling subsystem. The members of the team have been preparing the validation environment of XtratuM Next Generation (XNG) and LithOS, and specified the software validation plan of the hypervisor and the end-user validation strategy. The team is already developing and running the software stress tests as part of the performance validation of the multicore platform.
“I am proud of the great achievements that the De-RISC team have reached in these two years,” Paco Gómez-Molinero, coordinator of the project, said. “With hard work and enthusiasm, we managed to achieve the major project goals, and the team is highly motivated to continue with the positive development effort of the project”.
The validation activities will be one of the main focus of the project and the hardware and software tasks will proceed as expected to support the use cases.
derisc-project.eu/; www.gaisler.com/getgrlib; gitlab.bsc.es/caos_hw/hdl_ip/bsc_pmu/
Related articles
€8m project for Europe’s first RISC-V supercomputer chip
Codasip looks to hire 100 RISC-V engineers in Bristol and Cambridge
1092 RISC-V cores in AI accelerator for multichip PCIe card
Other articles on eeNews Europe
- Europe to extend investigation of Nvidia-ARM deal
- France in €6bn boost for semiconductors
- Europe invests €227m directly in tech startups
- Power breakthrough for neuromorphic AI
- Nordic ports TinyML to cellular IoT chip
- 14,336 ARM cores in chiplet-based waferscale AI engine
 If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News
If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News


